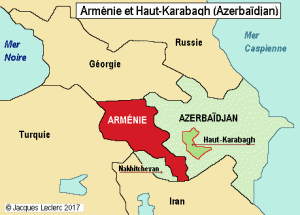
Armenia is a Transcaucasian (South Caucasus) nation bordered by Georgia to the north, Azerbaijan to the east, Iran to the south and Turkey to the west. It also borders the de facto republic of Nagorno Karabakh to the east and the Azerbaijani exclave of Nakhchivan to the south. It is therefore a landlocked state.
Geographical background
The climate is continental, and since the mountain ranges stop the influences of the Mediterranean and Black Seas, it includes hot summers and cold winters; rainfall varies greatly from area to area: along the banks of the Aras River is the driest area in the country.
Languages spoken
The Armenian language is spoken in the country in the Oriental variant, which is also widespread in the Armenian community in Iran. Several language minorities are widespread in the country and a large part of the Armenian population speaks Russian as a second language.
Human geography
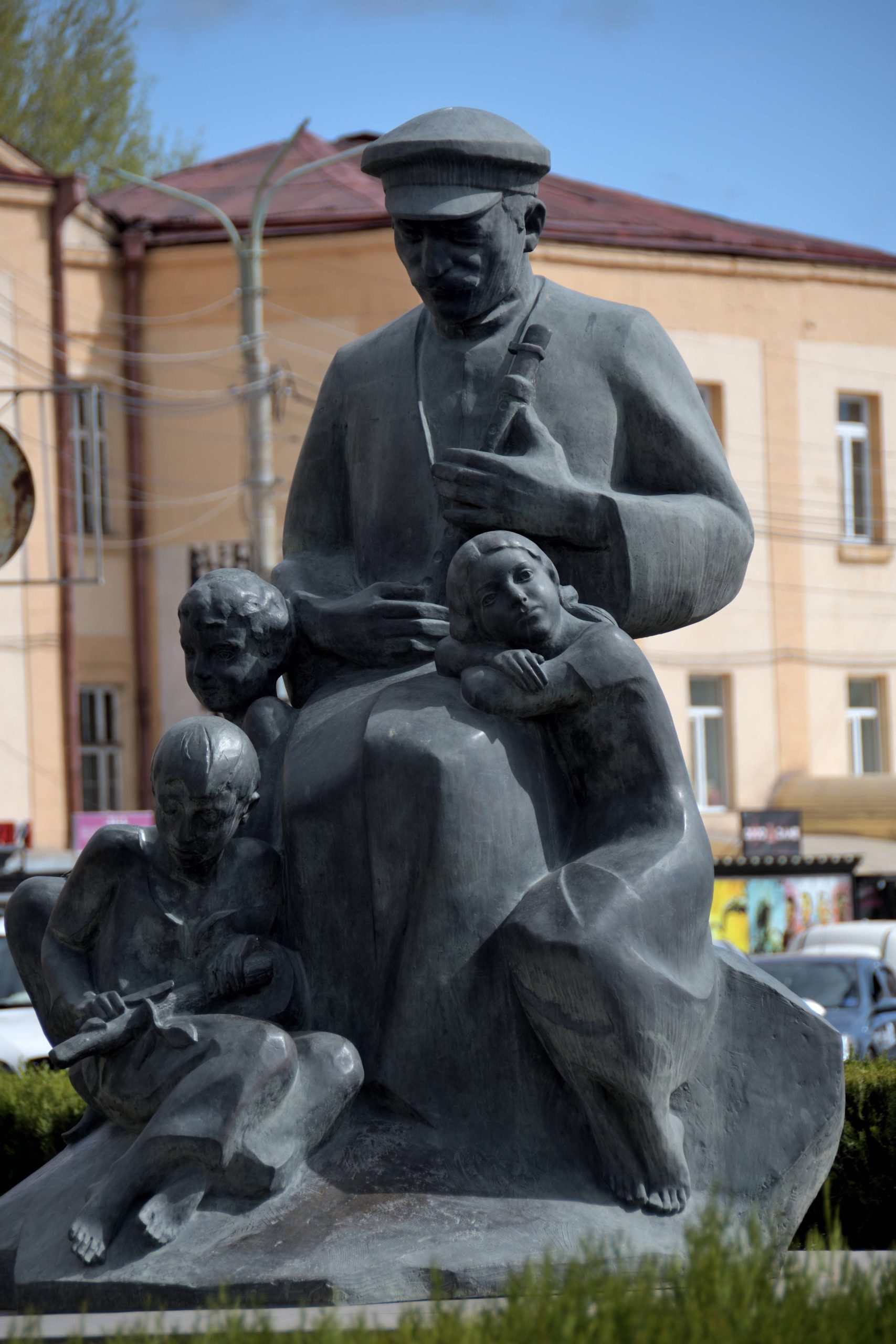
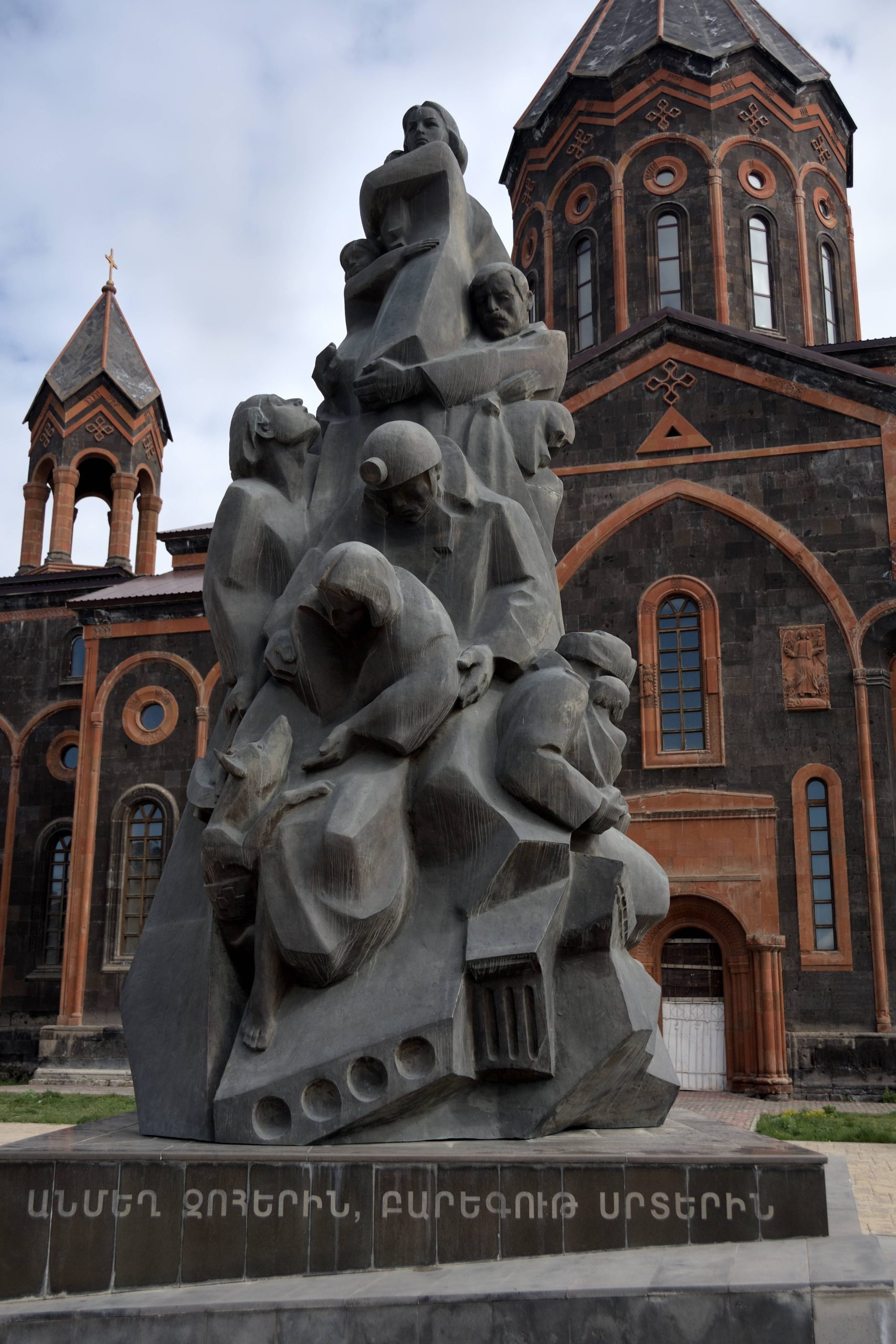
Culture and traditions
Written literature was born in the 5th century A.D. The fathers of Armenian literature were Mastots and Sahak the Great. In the 18th century, Mekhitarist literary culture spread. The main poets of recent centuries are the patriot Hovannes Tumanian and the diaspora intellectuals Arsciak Ciobanian and Hrand Nazariantz. In the contemporary music scene, mention must be made of the singer André (stage name Andreï Hovnanyan), Charles Aznavour and the US-based group System of a Down. The members are all originally from Armenia, and are descended from survivors of the genocide suffered by their people, which they talk about in many songs. Armenia is the first state in the world to introduce the study and play of chess as a compulsory subject in all schools, with the aim of creating a better society, respecting rules and developing strategies.
Economy
The primary sector employs 40 per cent of the population. Mainly wheat, barley, maize, potatoes, tobacco, vegetables, grapes and fruit are cultivated. Sheep’s milk gives the famous motal. However, Armenia is forced to import large quantities of foodstuffs because local production cannot meet the country’s needs. Mining of gold, copper, zinc, iron, silver and natural gas is also important. Armenia is a highly industrialised country. The industrial sector employs the most people. The food, paper, mechanical, electrical, textile, chemical, rubber, cement and tobacco industries are particularly important. The industrial sector suffered severely due to the economic blockade imposed by Azerbaijan in 1991. In 1994, the country then announced its decision to restore the Mdedzamor plants, the only nuclear station in the Transcaucasus region, which had been closed following the earthquake of ’88, to compensate for the decreased availability of energy. Armenia’s currency is the dram. Virtually all production, energy, mineral resources and transport are in foreign hands As far as transport is concerned, Armenia is criss-crossed by railway lines connecting it with Tbilisi (Georgia), Baku (Azerbaijan) and Kars (Turkey). Connections with Azerbaijan and Turkey are, however, disrupted due to the closing of the borders between the countries following the Nagorno-Karabakh war. The elections of 2018 totally changed the political landscape, leading to the appointment of Nikol Pachinian as prime minister. This enabled a whole series of legislative reforms and the beginning of a real fight against corruption. But the situation that arose in Armenia, first with the CoVid pandemic, then with the Karabakh war, greatly slowed down the democratisation of the country. In early elections in June 2021, following the armistice signed in November 2020 with Azerbaijan, Pachinian was confirmed as prime minister, but now the country faces a difficult reconstruction. The Covid19 pandemic is raging in Armenia: at the beginning of November 2021, less than 10 per cent of the 2.5 million inhabitants were vaccinated, and infections averaged 1,000 per week.
Sources:

















